Strong readers are both fluent decoders and skilled comprehenders. As teachers, we can develop strong readers by teaching our students the strategies they need to decode and comprehend text effectively.
Small group instruction is a great time to target both decoding skills and reading comprehension strategies.
If you struggle fitting both decoding and comprehension strategy work into your small group instruction, you’ve come to the right place!
There is a misconception that decodable texts can only be used to practice decoding, but they can actually be used for much more! For example, decodable texts can be used for fluency, high frequency word work, and to build reading comprehension.
In this blog post, I’ll share some activities you can use to build your students’ comprehension while using decodable texts during small group instruction!

What are decodable texts?
Decodable texts are carefully controlled texts that include specific phonics skills students are learning.
For example, a text focusing on the “long a” sound spelled “ai” will feature many words with this phonics pattern. This allows students to apply what they are learning in phonics directly within the text they are reading.
Here is an example from a decodable text found in my Nonfiction Decodable Safari Texts. The target phonics skill for this text is CVCe words. You’ll see there are multiple opportunities for students to apply what they have learned about the CVCe pattern!

If you want to learn more about using decodable texts, check out my blog post on this topic HERE.
Decodable texts and comprehension
Although the primary purpose of using decodable texts is to provide students practice reading specific phonics patterns in context, we can also build students’ comprehension through the use of decodable texts.
It’s important to incorporate comprehension activities when reading decodable texts because it provides students an opportunity to focus on the meaning of the text without the added struggle of decoding. Since the decodable text is aligned to the phonics skills that have been newly or previously taught, we know that students should be able to successfully decode those words. They won’t be struggling through words they don’t have the knowledge to decode, so some space in the brain is freed up to focus on comprehension.
Providing opportunities to practice comprehension within a controlled text also helps build students’ reading confidence.

Comprehension activities to use with decodable text
I’ll now walk you through some activities you can use with your students to build their comprehension while reading decodable texts!
Activity 1: Activate prior knowledge
Activating prior knowledge is a comprehension strategy that helps students connect their existing background knowledge to new information in the text.
Before reading, connect the text to students’ prior knowledge. For example, discuss what students know about frogs before reading a text about the Desert Rain Frog. When students read the text, they will think about what they already know as they learn new information.
If students don’t have much background knowledge on a topic, teachers can front load information about the topic prior to reading. Teachers can do this by reading a short text about the topic, or by showing a short video clip prior to reading the text.
Activity #2: Stop and check for understanding
Another comprehension activity to use with decodable texts is having students stop and check for understanding. Incorporate frequent pauses during reading to have students retell what they’ve read so far. This helps them monitor their own understanding and identify any points of confusion.
The number of times to stop and check for understanding within a text depends on the length of the text. In short decodable passages, instruct students to stop halfway. For longer texts, consider chunking the text into three or four parts and have students stop at each point to evaluate their comprehension and retell.

Activity #3: Use graphic organizers
Using graphic organizers is a great way for students to consolidate what they learn from the decodable text. Graphic organizers are visuals that help students organize information, identify key concepts, and build a deeper understanding of what they are reading.
Graphic organizers can be used before, during, and after reading to support comprehension.
There are many different types of graphic organizers you can use with decodable texts! Here are some examples:
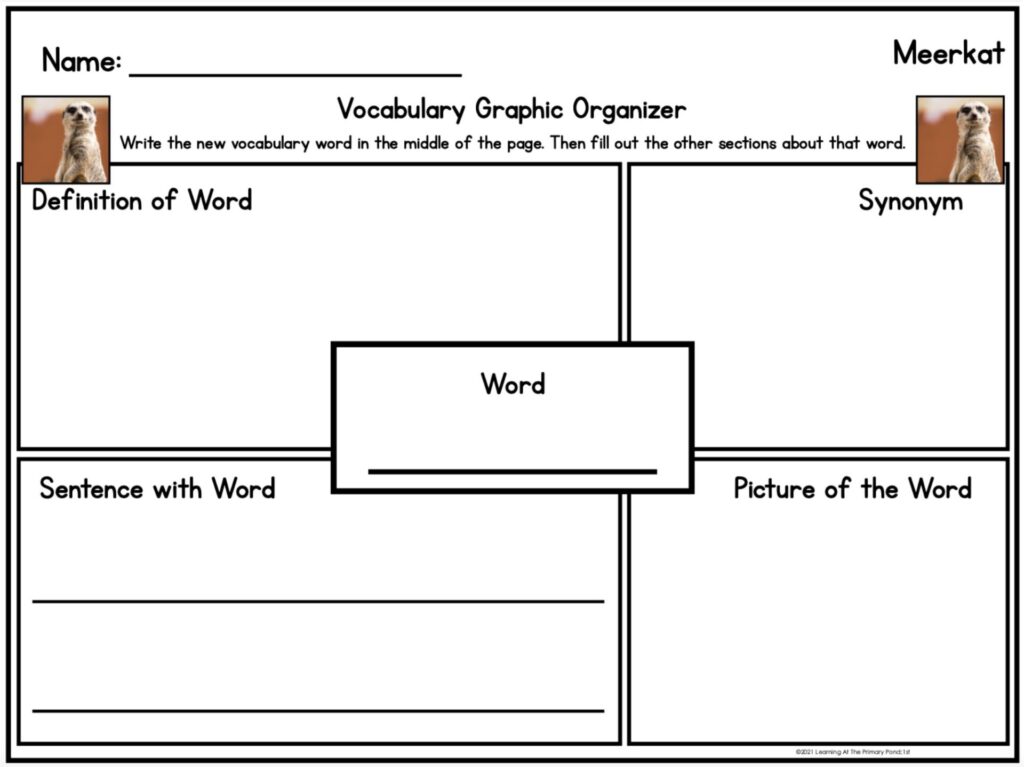
- A KWL Chart is a tool to use before and after reading. A KWL chart helps students activate prior knowledge (‘Know’), identify learning goals (‘Want to Know’), and reflect on what they’ve learned (‘Learned’).
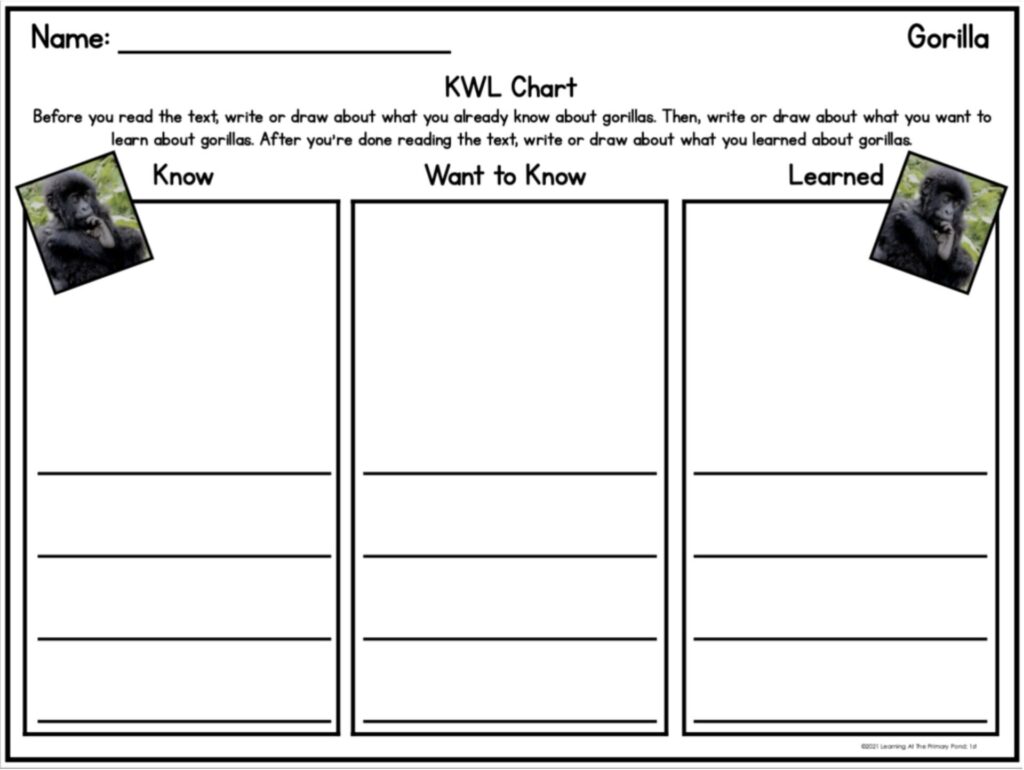
- A 3-2-1 Graphic Organizer is a fun way for students to quickly reflect on what they have learned by listing 3 things they learned, 2 interesting facts, and 1 question they still have.
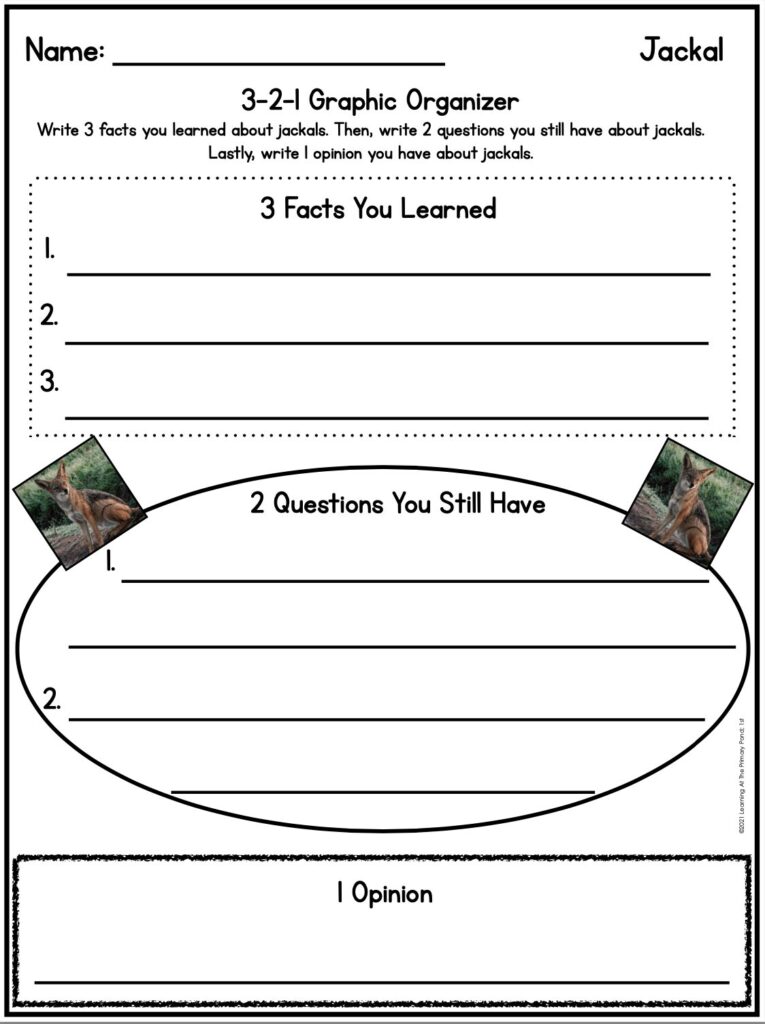
- A Vocabulary Graphic Organizer is a great way to build students’ vocabulary knowledge. This organizer helps students deepen their understanding of new words by defining them, finding synonyms, using them in sentences, and drawing pictures.
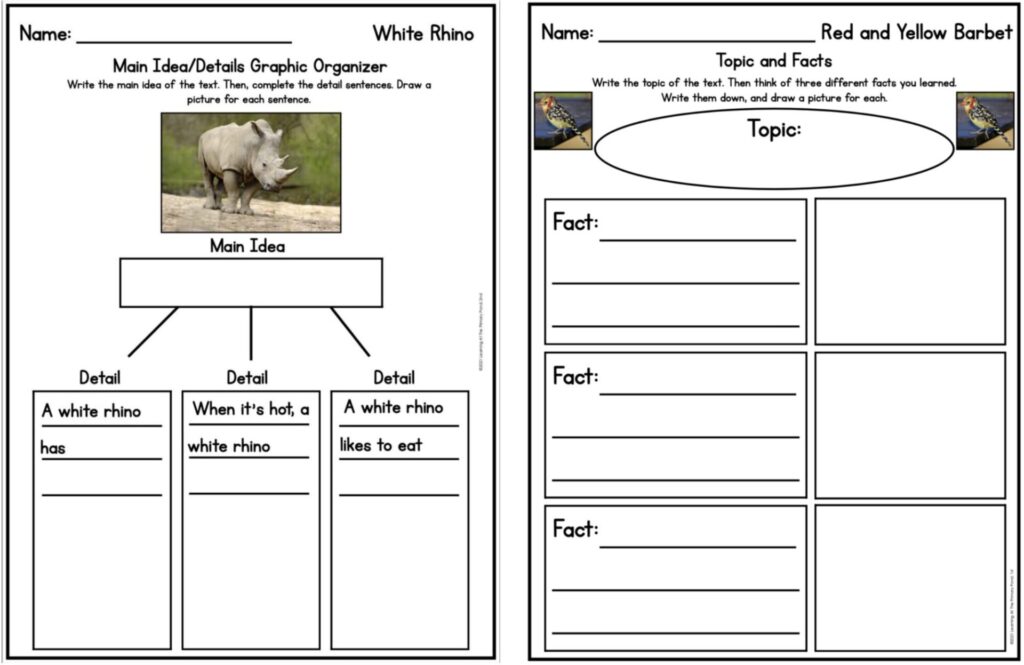
- A Main Idea and Details Graphic Organizer helps students identify the main idea of the text and the key details that support it. Similarly, a Topic and Facts Graphic Organizer focuses on identifying key facts learned from the text.
- A Compare and Contrast Graphic Organizer helps students connect new information to their prior knowledge by comparing and contrasting similar topics.

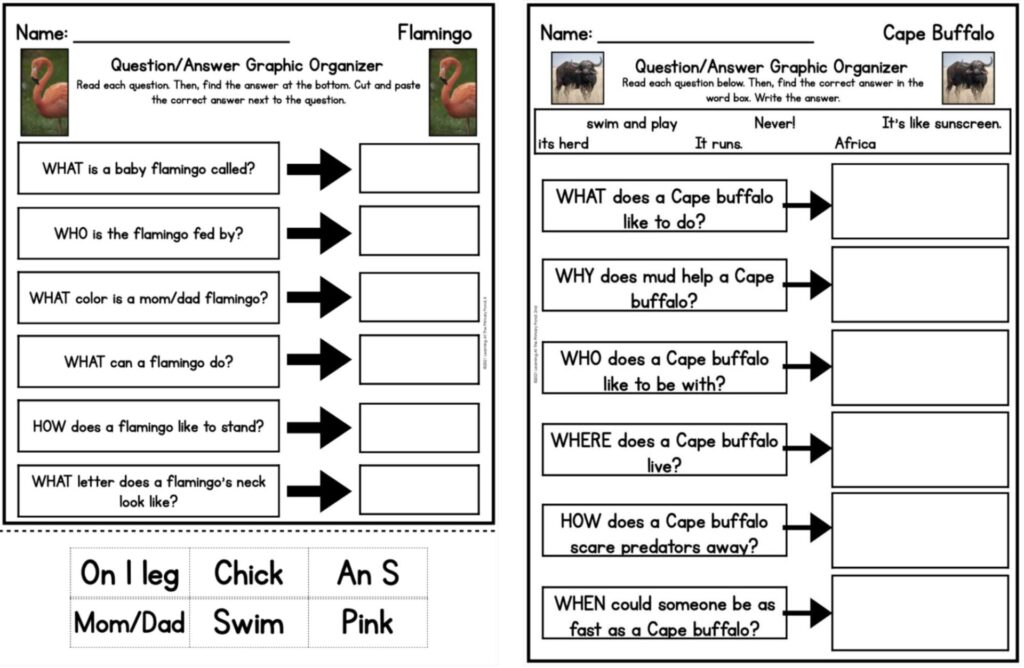
- A Question and Answer Graphic Organizer focuses on answering specific questions related to the text. It can be scaffolded for different learning levels.
Activity #4: Question generation
Question generation is a fun, highly effective way to get students thinking about what they have read. In this activity, students get to pretend to be the teacher. Students come up with questions about the text, and then they ask their peers to answer their questions!
When using question generation as a comprehension activity, be sure to model for students the type of questions to ask. Model question stems like “Who/What is the text about?” and “Why did this happen?”.
You will also want to model appropriate responses to their peers’ questions. This is a great time to remind students to reference the text when answering questions!
Activity #5: Write about the text
Writing about the text helps students think about what they have read after they finish reading. This could include writing summaries, answering questions, or even creative writing inspired by the reading.
Teachers can use students’ writing as an assessment to monitor how well they are comprehending what they read! Writing tasks can also be scaffolded for all levels.

Decodable Safari Texts
There are many more comprehension activities you can use with decodable texts!
Are you ready to start incorporating comprehension activities into your small group instruction around decodable texts? If so, I have the right product for you!
My Nonfiction Decodable Safari Texts for kindergarten through second grade provide engaging lessons, assessments, and activities to help you implement these strategies effectively. You can check them out here at my TPT store.
These texts:
- Come with a lesson plan for each passage
- Include lots of text features
- Have a comprehension assessment and vocabulary work
- Provide a graphic organizer
- Include a writing prompt
And best of all, you’ll be able to implement all of the comprehension activities in this blog post while using these decodable texts!


Happy teaching!